
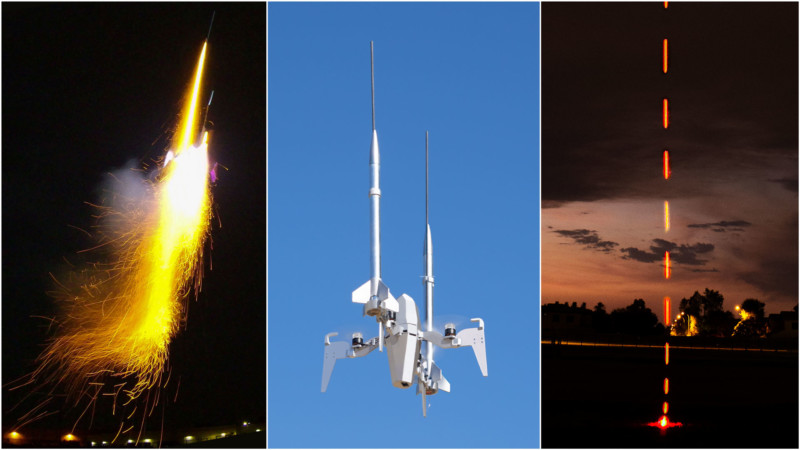
A Rapid Ascent Drone, or RAD, is basically an electric rocket ship. For now, they can be used to make unusual drone light shows that can replace fireworks and provide unique light painting opportunities, but the creator of the concept believes they may be able to eventually replace rocket ships.
Rammaxx is a RAD manufacturer that built its concept by working with small, electric rapid ascent rockets for electronic fireworks shows. The company built its autonomous drones with the ability to work in “swarms” and create unusual visual spectacles thanks to their ability to ascend extremely quickly and stay at altitude long enough to play a light sequence before returning to base. Rammaxx says that the rapid ascent capability is achieved via powerful motors, a streamlined hull, and special guidance fins.
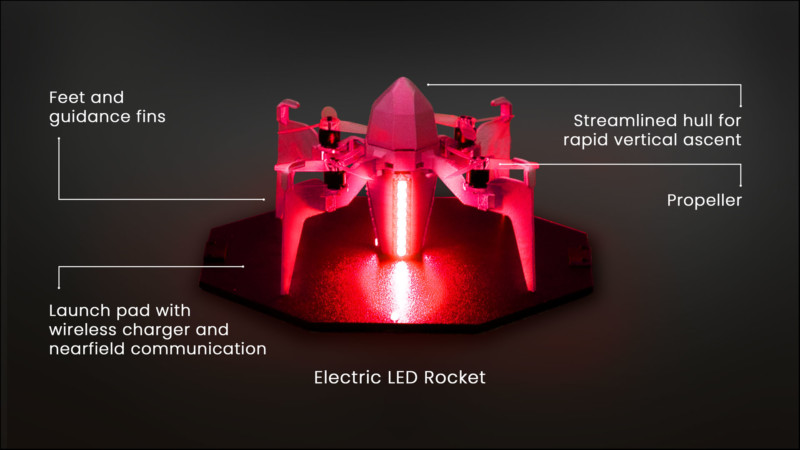
“Rammaxx can be configured to ascend quickly, and noisily, or to ascend more slowly and quietly,” the company explains. “The system can work with one rocket, or with a small swarm of them, creating unique and highly — via App — configurable light displays for any occasion.”
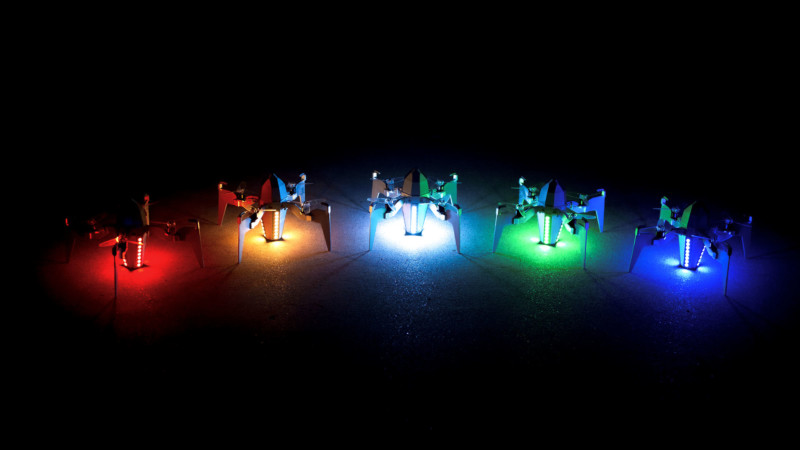
A Rammaxx RAD drone can recharge wirelessly on a dedicated launch pad that is connected to a bus system. Up to five launch pads can be connected together to create more complex aerial light displays.
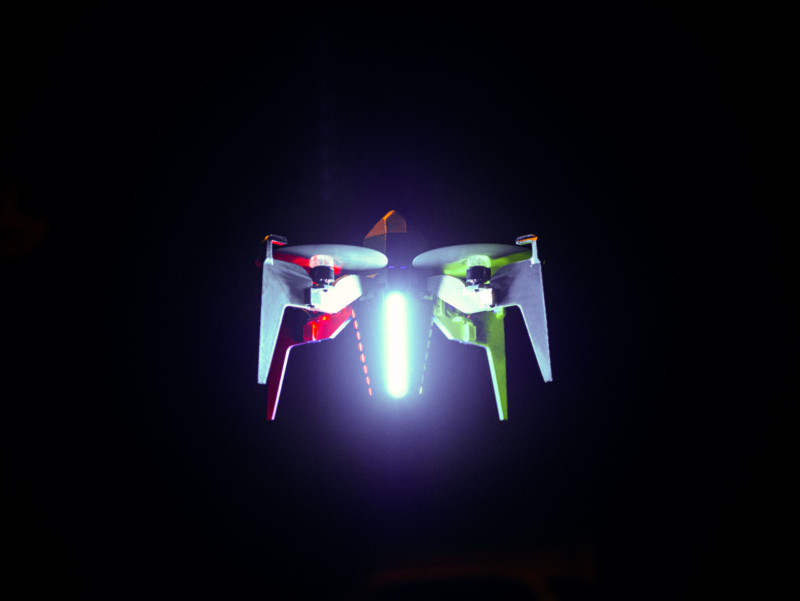

The drones weigh a scant three ounces (90 grams) and can fly for one minute with full LED power that can project light at up to 3,000 lumens of brightness. While that might not seem very long, the drones can land and recharge in just 30 seconds before they are ready to fly again.

These rapid ascent drones can fly into the air at a blistering 80 miles per hour (150 kilometers per hour) in what Rammaxx calls “rapid and noisy ascent,” but are also capable of doing so slower and more quietly.
These RADs are different than traditional drones in a number of ways. While they are battery-powered, Rammaxx’s CEO and Co-Founder Dan Lubrich tells PetaPixel that, unlike other drones, these are optimized for vertical flight and the electric circuits in them are optimized for a short duration but very high power, rather than long duration and low power.
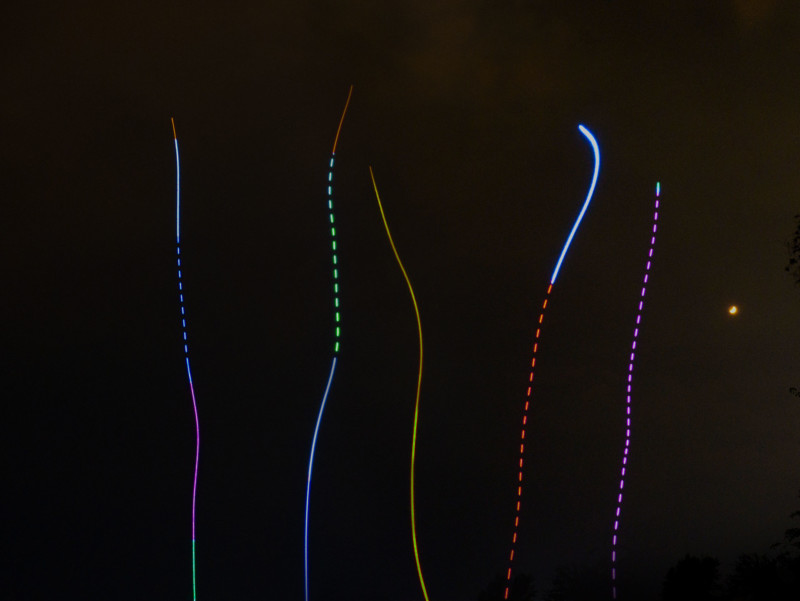

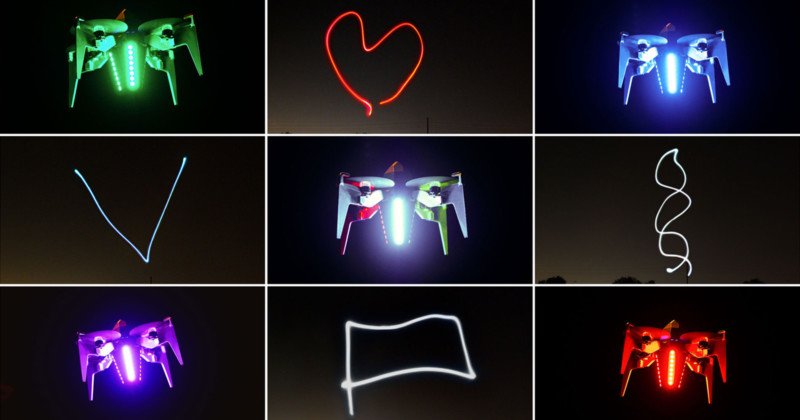
Beyond a typical aerial light display, the RADs can also allow for light painting if exposure is set for at least five seconds. The shapes can be programmed into the app the company says that it is working on showing how to do this in upcoming tutorial videos. But in short, Lubrich says a user can draw on the screen to show the pattern and that shape can be uploaded to the drone and it will fly that path accordingly.
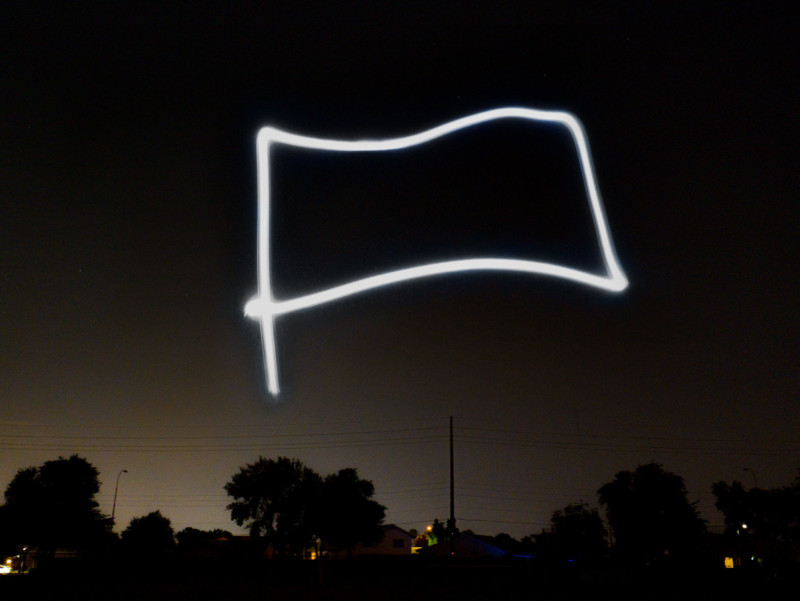
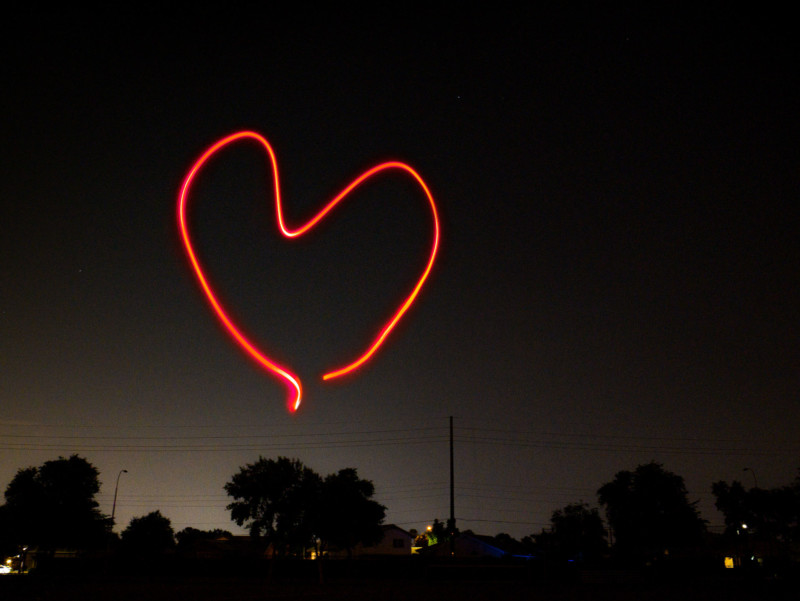
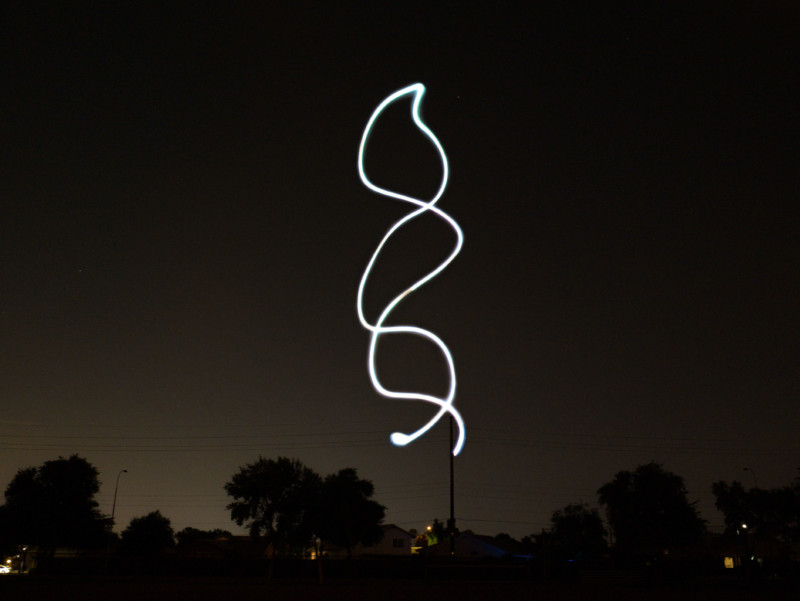





“Once launched, the pilot is out of the loop, so they can focus on taking pictures, or just enjoying the show. We are working on putting together a more detailed video that focuses more on the light show aspect of the system,” Lubrich says.
Lubrich has greater ambitions for its technology beyond light shows and tells PetaPixel that he believes RAD technology can assist in space exploration.
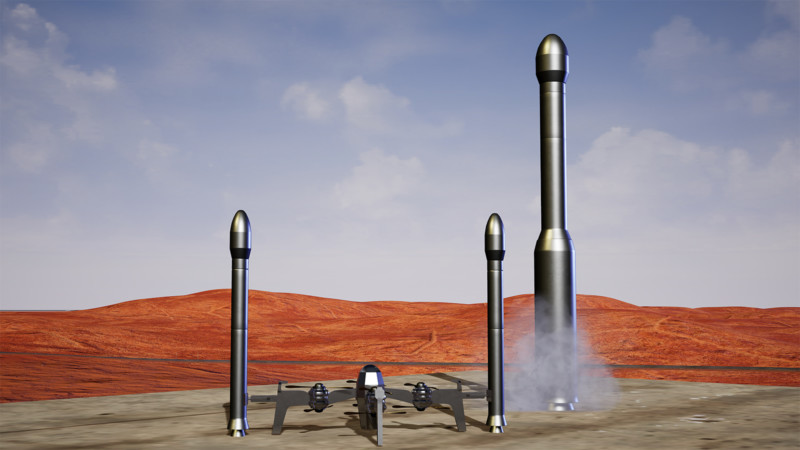
He says that the large size of a first-stage rocket is the main reason that space flight is so expensive, dangerous, and environmentally unfriendly. To address this, the Rammaxx RAD concept is a large powerful drone based on the design of the current light painting RADs. Early projections show that it should be able to accelerate with a rocket to around 300 miles per hour (500 kilometers per hour) up to an altitude of around 15,000 feet (5,000 meters).
“The important aspect for space flight isn’t so much the altitude gained — although that also helps a little bit — but rather the speed gained during the ascent,” he explains. “So, much less rocket fuel is needed to get off the ground and up to a few hundred miles per hour. That allows for smaller, cheaper, safer, and cleaner space rockets.”

“When flying as a swarm with a rocket in tow, we envision the drones to act as one super drone, rather than a true swarm, meaning the flight controllers of the drones link together creating one large drone with many rotors out of lots of small ones,” Lubrich says. “This is so that the flight is 100 percent precise.”

If the drones were independent, even if they were connected to each other via the rocket, there could be small differences in the way that they fly, which could create problems due to them being physically connected, Lubrich explains. Instead, there would be one designated master drone in the swarm that would — when all of them are linked together — control all the drones and turn the swarm into one large super drone, all controlled by the same master flight controller.
“Once the rocket has launched and the physical link between drones is broken, the software link is broken too and the rapid ascent drones independently descend back to the launch pad, staying out of each other’s way as they do so,” Lubrich says.
Lubrich and Rammaxx envision a future where these RADs would allow for much smaller ground to space rockets where the current first stage of space flight could be nearly completely eliminated. The space flight-enabled RADs would feature eight rotors with 300 horsepower each for a total of a 2,400 horsepower drone that is capable of carrying 13,000 pounds of payload 15,000 feet in 90 seconds. The RAD’s four-minute battery life would give it plenty of time to safely return to Earth afterward.
Ramaxx has already completed a few small-scale tests of the concept as seen in the photos below.
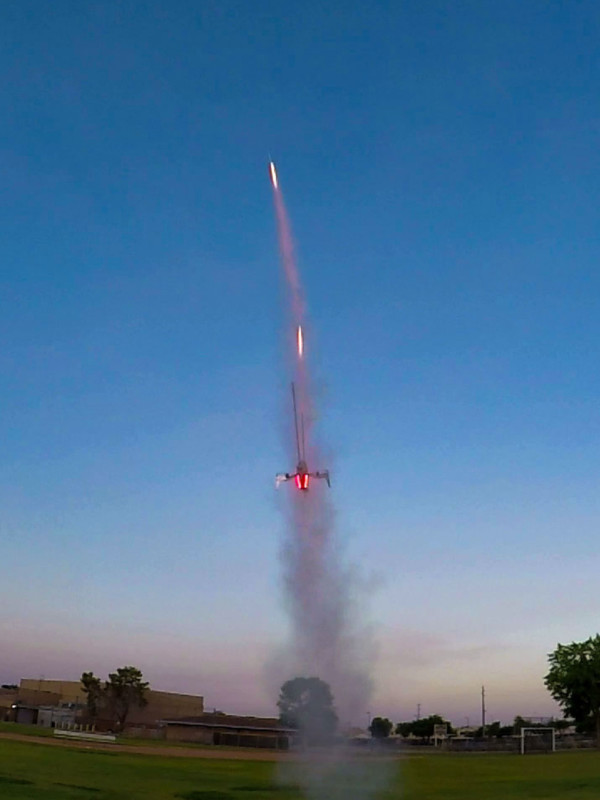
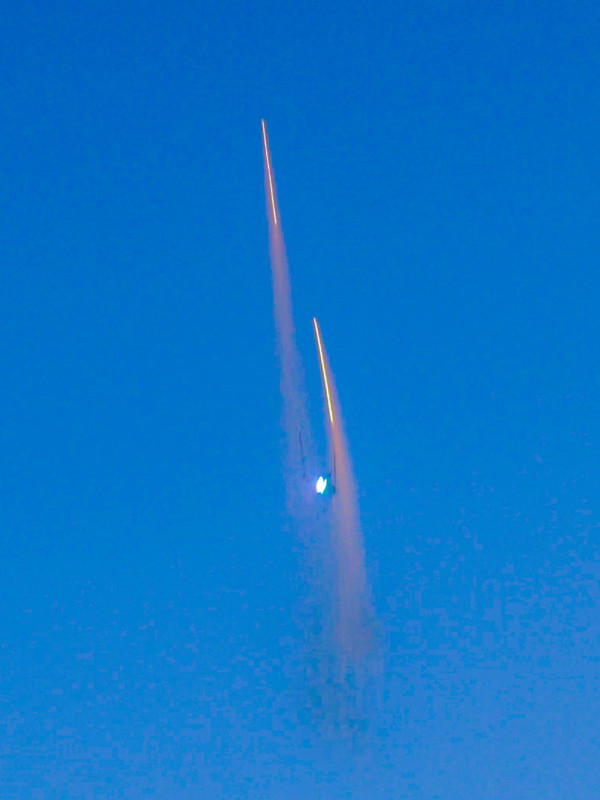
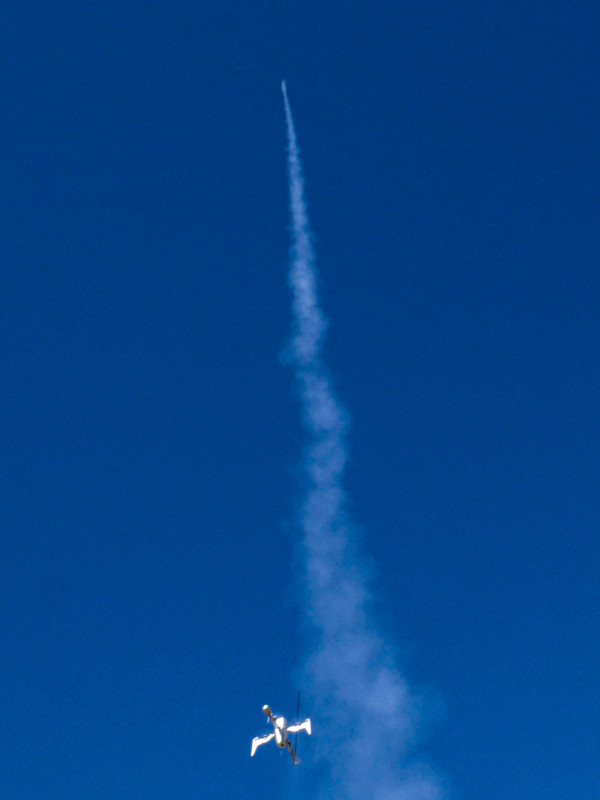
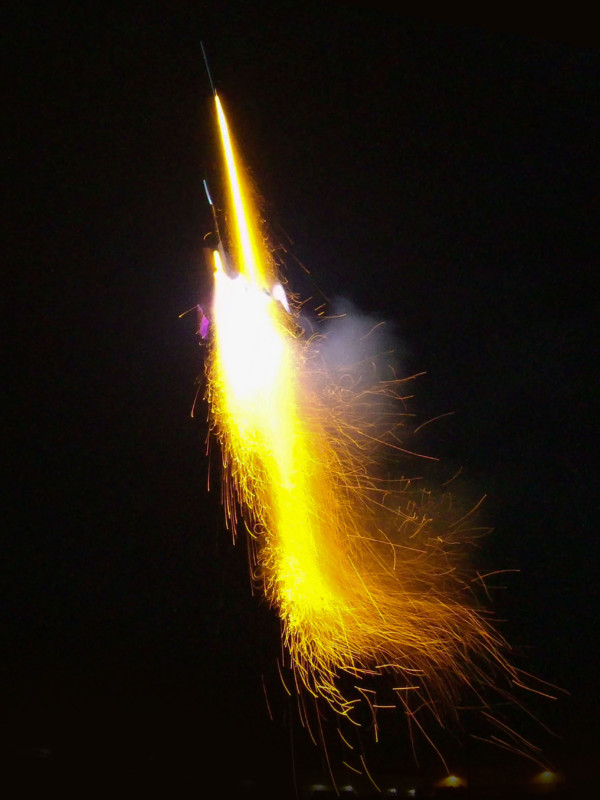




What is now just a neat way to provide a firework alternative and a different light painting experience could be a revolutionary shift in how humans approach space flight. Thanks to successful small-scale tests, Lubrich believes it is only a matter of time.
Image credits: All photos courtesy of Rammaxx and used with permission.